Ccf meaning medical – Delving into the realm of cardiology, we unravel the intricacies of congestive cardiac failure (CCF), a condition that profoundly affects the heart’s ability to pump blood effectively. This comprehensive guide delves into the pathophysiology, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment, and management of CCF, providing a holistic understanding of this prevalent cardiovascular ailment.
CCF Symptoms and Signs: Ccf Meaning Medical
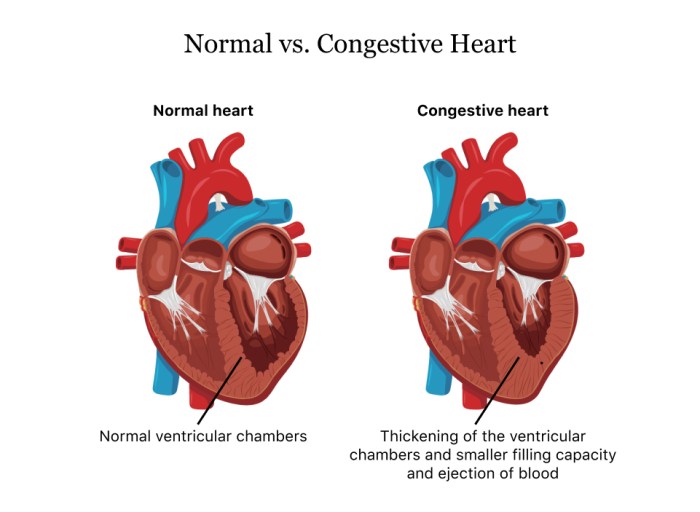
Congestive heart failure (CCF) is a condition in which the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can lead to a buildup of fluid in the body, which can cause a variety of symptoms.
The most common symptoms of CCF include:
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Edema (swelling in the feet, ankles, and legs)
Other symptoms of CCF can include:
- Rapid weight gain
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion
Physical Signs
In addition to the symptoms listed above, CCF can also cause a number of physical signs. These signs can include:
- Jugular venous distension (JVD)
- Pulmonary crackles
- Hepatomegaly (enlarged liver)
- Ascites (fluid in the abdomen)
CCF Causes and Risk Factors
Congestive heart failure (CCF) is often caused by underlying conditions that damage the heart or impair its ability to pump blood effectively. These conditions include:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): CAD occurs when the arteries supplying blood to the heart become narrowed or blocked, reducing blood flow to the heart muscle.
- Hypertension: High blood pressure can strain the heart, causing it to enlarge and weaken over time.
- Valvular heart disease: Problems with the heart valves, such as stenosis (narrowing) or regurgitation (leaking), can disrupt blood flow through the heart.
In addition to these underlying causes, certain risk factors can increase the likelihood of developing CCF. These include:
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Family history of heart disease
- Advanced age
Modifiable risk factors, such as smoking and obesity, can be managed through lifestyle changes to reduce the risk of CCF. Non-modifiable risk factors, such as age and family history, cannot be changed but can be monitored and managed to mitigate their potential impact on heart health.
CCF Treatment Options
Congestive heart failure (CCF) is a serious condition that requires prompt and appropriate treatment. The primary goal of CCF treatment is to improve cardiac function, reduce fluid retention, and prevent complications. Various treatment options are available, ranging from medications to lifestyle modifications and surgical interventions.
Medications
- Diuretics help remove excess fluid from the body, reducing fluid retention and improving cardiac function.
- ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs) relax blood vessels, reducing blood pressure and improving blood flow to the heart.
- Beta-blockers slow the heart rate and reduce the force of heart contractions, decreasing the heart’s workload.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Reducing salt intake helps decrease fluid retention and improve cardiac function.
- Losing weight can reduce the burden on the heart and improve overall health.
- Regular exercise can strengthen the heart and improve its efficiency.
Surgical Interventions, Ccf meaning medical
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) improves blood flow to the heart by bypassing narrowed or blocked arteries.
- Heart valve replacement or repair corrects abnormalities in heart valves, improving blood flow and reducing strain on the heart.
- Ventricular assist devices (VADs) are mechanical pumps that help the heart pump blood, providing support during severe heart failure.
The choice of treatment for CCF depends on the severity of the condition, the patient’s overall health, and their individual preferences. A combination of therapies is often necessary to achieve optimal results.
Concluding Remarks

Comprehending the complexities of CCF empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their health, adopt preventative measures, and actively participate in managing this condition. By integrating lifestyle modifications, adhering to treatment plans, and maintaining regular medical check-ups, patients can optimize their quality of life and navigate the challenges posed by CCF.
FAQ Resource
What is the primary cause of CCF?
Coronary artery disease, characterized by the buildup of plaque in the arteries supplying blood to the heart, is the leading cause of CCF.
Can lifestyle modifications help prevent CCF?
Absolutely! Regular exercise, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and managing blood pressure and cholesterol levels can significantly reduce the risk of developing CCF.
What are the early warning signs of CCF?
Shortness of breath, especially when lying down or exerting oneself, fatigue, and swelling in the legs, ankles, and feet are common early indicators of CCF.